Green tea health benefits
Written by Sneh Chaudhry on October 25, 2023
Green tea, derived from the Camellia sinensis plant, is known for its unfermented nature and minimal processing. Green tea is rich in antioxidant content. With lower caffeine levels compared to other teas, it’s often considered the healthiest type of tea. But what makes green tea special, and how much should one consume daily for optimal well-being?
The magic of green tea lies in its wealth of polyphenols, particularly catechins. Among these, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) takes the lead and is responsible for most of green tea’s acclaimed health benefits. Here are some key benefits associated with regular consumption of green tea:
Lower blood pressure
Green tea’s catechins may have a short-term impact on reducing blood pressure, particularly in individuals with systolic blood pressure over 130 mm Hg, according to a 2014 study published in the European Journal of Nutrition.
Better blood sugar control
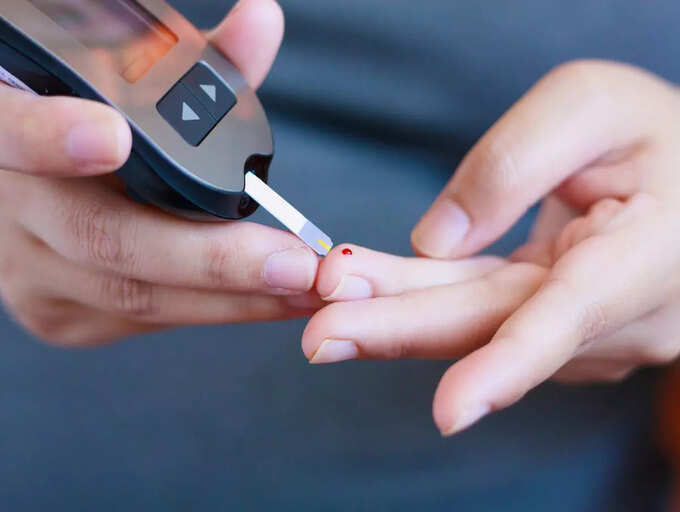

Research suggests that green tea can enhance blood sugar management and insulin sensitivity. A 2021 study involving adults in China found that those who drank green tea every day were less likely to develop diabetes, compared to those who did not drink green tea or drank other types of tea. The findings of the study were published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Improved relaxation and mood

L-theanine found in green tea promotes relaxation and cognitive function. In a 2017 review published in the journal Phytomedicine, researchers found that drinking green tea could help limit anxiety, and improve memory as well as attention span. A 2022 study found that adolescents (12-18 years old) who drank 6 cups of decaffeinated green tea a day for 6 weeks had less stress hormones and improved depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms.
How much green tea should I consume?

While there are several benefits associated with green tea consumption, it is important to note that many of them come after the consumption of 6 cups a day or through green tea extract supplements. In case you take supplements, it is important to note that higher concentrations of EGCG and catechins can lead to side effects such as stomach upset, liver toxicity, insomnia, skin rashes, and blood pressure spikes.
Risks associated with excessive consumption








